Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can be fatal or cause permanent damage to your health.
CO is produced when carbon fuels don't burn completely. It has no smell or taste, and, in large quantities, it can kill very quickly.
How is carbon monoxide produced?
Carbon monoxide is hard to detect because it has no smell, taste or colour. This also means that it is easy to inhale without realising.
Carbon monoxide is produced when fuels such as gas, oil, coal and wood do not burn fully.
When a fire burns in an enclosed room, the oxygen in the room is gradually used up and replaced with carbon dioxide. Following a build-up of carbon dioxide in the air, the fuel is prevented from burning fully and it starts to release carbon monoxide.
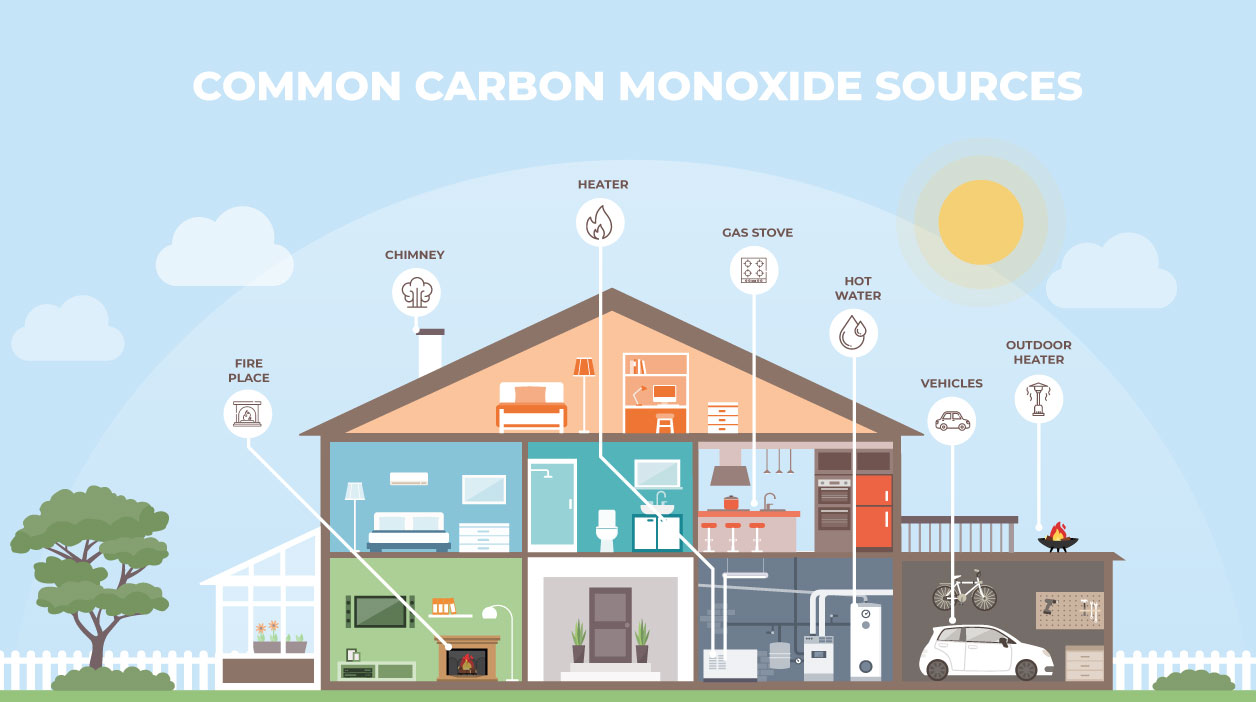
Causes of carbon monoxide poisoning
Gas, oil, coal and wood are all fuel sources that are used in many household appliances, including:
- gas fires
- central heating systems
- water heaters
- cookers
- open fires
If the fuel in these appliances does not burn fully, carbon monoxide (CO) gas is produced.
Other ways that carbon monoxide can build up
The build-up of carbon monoxide can also be as a result of any of the following:
- Indoor use of a barbecue grill or outdoor heater
- Using cooking appliances for heating purposes
- Enclosed or unventilated spaces - burning fuel in an enclosed or unventilated space, where there are no air vents, windows or doors left open or ajar
- Faulty or damaged appliances - heating or cooking
- Heating appliance not maintained or serviced
- Badly ventilated rooms - sealed windows, no air bricks
- Blocked chimneys or flues - birds nests, fallen bricks, growing vegetation, bad DIY
- Poor or improper installation or use of appliances - such as cooking and heating devices
- Running engines such as cars or lawnmowers in garages
- Old appliances that have not been serviced or looked after properly
- Paint fumes - Fumes from cleaning fluids and paint removers that contain methylene chloride (dichloromethane) can also cause CO poisoning
Danger signs
Danger signs that CO may be leaking include:
- yellow or orange flames where there should normally be blue ones
- sooty stains on the walls around fires and water heaters. You could also be poisoned by CO if you share a wall or chimney with a house that has a CO leak, even if your own house does not have one




